Water change in aquarium
A water change in aquarium is a basic maintenance procedure. However, it turns out that many beginning aquarists do not fully understand the importance of regular water changes and do not know how to do it properly. Some of them think they simply need to pour all water out of the tank and fill the tank with fresh one. Plus rinse all the media and clean filters. This is a very serious mistake, which usually leads to disease and death of fish, as well as a whole bunch of other aquarium maintenance problems.
Why are water changes important?
In the aquarium organic matter accumulates all the time. It consists of animal feces, uneaten food and parts of plants. It accumulates in the filters and substrate, where it is gradually broken down by bacteria. The simple minerals released in this process end up in the aquarium water and become available to aquatic plants and algae.
The more organic matter in the tank, the more such substances are in the water, deteriorating its chemical parameters. In extreme cases, this can result in fish poisoning, or prolonged stress leading to decreased fish immunity and increased susceptibility to pathogens. Thus, water changes are intended to reduce the concentration of accumulated chemical compounds in the aquarium water and ensure good water chemical parameters.
Frequency of water changes in the aquarium
It is recommended to do water changes regularly. In most cases once a week. However, in aquariums with smaller fish populations, you can make less frequent changes. But some tanks might have fish in high densities or fish that belong to filthy species, e.g. goldfish, wood-eating plecos, large catfish, etc. If this is the case, you may need to do water changes more often. By observing your tank, you can easily determine what frequency of water changes will work best for it.
How much water to change?
Typically, experts recommend water changes of 20-30% of the aquarium volume. If you have delicate fish, it is better to make smaller changes, but more often. Also, in smaller aquariums it is better to change less water, but with more frequency. A large water change in a small aquarium can upset the biological balance quite significantly.
How to prepare water?
Many aquarists set aside water intended for change in buckets or other containers for a period of about 24 hours. During this time, chlorine used to disinfect tap water will evaporate from the water. At the same time, the water temperature will increase. However, with larger aquariums, it is not always possible to set aside enough water for water changes.
Then you can use tap water. But remember that it is always a good idea to use products such as Antychlor to neutralize chlorine or Esklarin with aloe to condition the tap water. For tanks with black water I recommend Blackclarin, which is enriched with peat extract, and for shrimp tanks – Shrimp Guard, which apart from its conditioning function supports moulting process in crustaceans and regulates their metabolic processes. Another good choice will be Supreme, which combines the properties of the previous two. It neutralizes heavy metals and protects fish’s skin, gills and eyes against aggressive influence of fresh water. Moreover, the addition of aloe vera accelerates the regeneration of damaged epidermis.
Also, remember that tap water is cold. That’s why you shouldn’t do too many water changes so as not to drastically lower the aquarium water temperature.
Aquarium water change versus other maintenance tasks
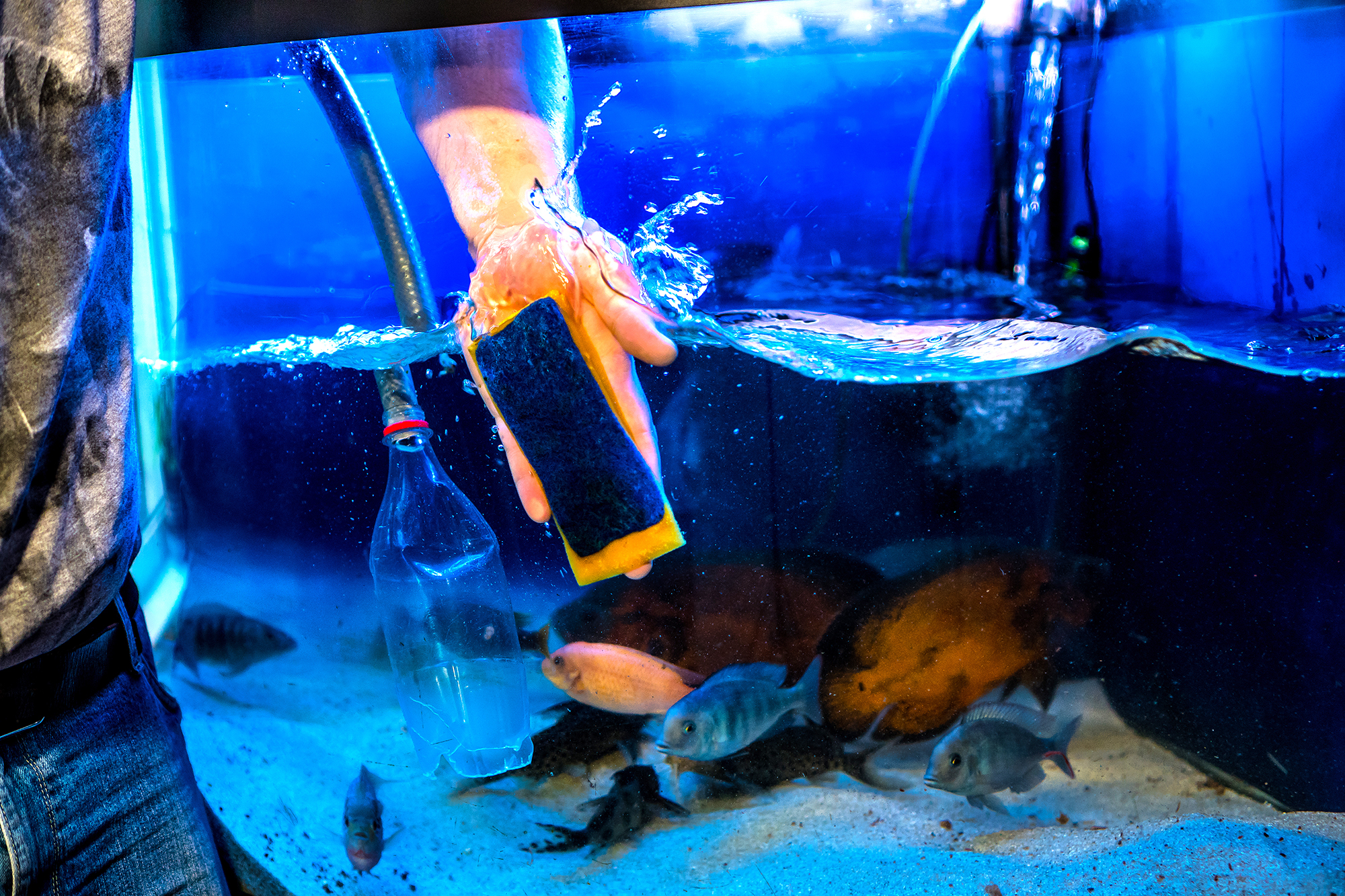
During water change, it’s a good idea to do other maintenance procedures. Before you start changing the water, turn off the heater and filters. Clean the glass of algae and sediment. Use a scrubbing pad or regular dishwashing sponge to do this. Only then can you start draining the water. When draining the aquarium, you can simultaneously desludge the bottom of the aquarium to get rid of accumulated organic sediment. You can use a professional desludger or make one from a cut PET bottle, which you can attach to the end of the hose.

If the aquarium has special substrate for aquatic plants, instead of classic desludging that strongly interferes with the substrate, you can remove the sediment with a small hose that is moved vigorously over the bottom.
A water change is also a good time to rinse mechanical filter sponges, perform plant pruning and remove damaged or algae-infested leaves.
On the second day after water change you can apply products with bacteria Bacto Active and Nitri-Active. Bacteria present in Bacto-Active are responsible for breaking down organic matter. The ammonium ions released during this process are utilized by nitrifying bacteria. Other mineral compounds dissolved in the water become available to aquatic plants, and the excess is easily removed during regular water changes.
Nitri-Active introduces selected strains of nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria into the aquarium. It is intended for use in young and mature tanks If used regularly, it ensures biological balance and supports self-cleaning processes in an aquarium.